Gene expression
What is a gene?
1941 George Wells Beadle & Edward Lawrie Tatum proposed the one gene - one enzyme (polypeptide) concept
Genes act by regulating distinct chemical events
First clear understanding of how genes work to produce phenotype
Neurospora crassa life cycle
http://users.rcn.com/jkimball.ma.ultranet/BiologyPages/N/Neurospora.html
Advantages of Neurospora for studying genetics
Can be grown quickly on simple culture medium.
Sugar, inorganic salts, one vitamin (biotin)
Spends most of life cycle in the haploid condition
So recessive mutations will show up in its phenotype
No need for test crosses
Can be asexually propagated in large numbers by conidia (asexual spores)
Can be mated to produce ordered tetrads
Life cycle of Neurospora crassa
Have two mating types (like sexes)
A and a
Matings occur only between two mycelia of differing mating types
Can be crossed by placing two types of mycelia on the same plate
Mycelia fuse, then nuclei fuse to form diploid zygote
Diploid zygote undergoes two stages of meiosis, followed by one mitotic division
These cell divisions occur in a narrow tube called the ascus (spore sac)
Which causes the meiotic and mitotic products to remain in order (ordered tetrads)
Thus, if the zygote nucleus is heterozygous for a gene (shown here as a and A) and there is no crossing over near that locus during meiosis I
The ascus will end up with four spores at one end containing one allele (a) and four spores at the other end containing the other allele (A)

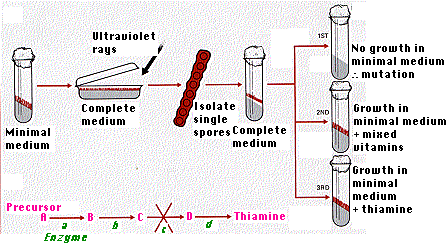
Experimental protocol
Grew normal (“wild-type”) Neurospora on minimal medium (sugar, inorganic salts, one vitamin (biotin)
Induced mutations in some conidia by exposing them to ultraviolet rays
Germinated and grew individual irradiated spores on a "complete" medium (enriched with various vitamins and amino acids)
Did crosses
Mated mycelium with spores of the other mating type
Dissected out ascospores individually and plated each one on complete medium.
Tested progeny on minimal medium
Subcultured clones of each of these genotypes on minimual medium (1st in figure), observed outcome
Sometimes grew on minimal medium; sometimes didn't.
Evaluated which functions were missing
When a genotype could not grow on minimal medium
Subcultured clones of genotype onto various media (2nd culture tube in figure) that differed in the composition of nutritional supplements (sugars, amino acids, vitamins, salts)
Eventually, each mutated strain was found to have acquired a need for one nutrient
For example, in 3rd culture tube in figure, fungus needs added vitamin thiamine
Interpretation
Beadle and Tatum reasoned that radiation had caused an allele at a gene that permits the synthesis of thiamine from the simple ingredients in minimal medium to mutate to an allele that does not.
The mutation altered a gene so it could no longer produce the normal enzyme, resulting in a physical symptom (phenotype), like the need for nutritional supplements.
One gene ŕ one enzyme
Further experimentation
Eventually deduced the thiamine synthesis pathway
By adding different precursors of thiamine, one at a time, to the culture medium, they narrowed down the defect to the absence of a single enzyme.
If they added to the minimal medium any precursor past that enzyme in the pathway, growth occurred.
If they added a precursor before that blocked step, growth did not occur
For their work, Beadle and Tatum shared, with J. Lederberg, the 1958 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine.
Class activity
Here’s a table of an experiment with Neurospora that is like Beadle’s and Tatum’s
Nutritional mutants were isolated from “wild-type” Neurospora
These responded to additions to minimal media be growth (+) or lack of growth (-)
Given the following responses of single gene mutations
Diagram a metabolic pathway consistent with the data
Indicate where the pathway is blocked in each mutant strain
|
|
Supplements added to minimal medium |
|
||||
Mutant strain |
citrulline |
GSA |
arginine |
ornithine |
glutamic acid |
|
1 |
+
|
-
|
+
|
-
|
-
|
|
2 |
+
|
+
|
+
|
+
|
-
|
|
3 |
+
|
-
|
+
|
+
|
-
|
|
4 |
-
|
-
|
+
|
-
|
-
|
|
Analysis
All strains rescued by arginine
Arginine is “end product”
Which strain rescued by only arginine?
Strain 4
Strain 4 mutated at gene converting precursor D to arginine
Gene d
Which strain rescued by arginine or another compound?
Strain 1 – rescued by arginine or citrulline
Mutated at gene converting Precursor C to citrulline
Gene c

Which strain rescued by arginine, citrulline, or another compound?
Strain 3 – rescued by arginine, citrulline, or ornithine
Mutated at gene converting Precursor B to ornithine
Gene b
Which strain unaccounted for?
Strain 2 – requires only GSA for rescue
Mutated at gene converting Precursor A to GSA
Gene a
What is precursor A?
Could be glutamate
No strains rescued by glutamate
Wildtype pathway
Today’s view of genes
Beadle and Tatum thought of a gene as an physical entity that produced an enzyme
Or, more broadly, a protein
However, we now know that some proteins have multiple subunits, and consist of two or more polypeptide chains
Polypeptide chain is chain of amino acids
One polypeptide can mutate while others remain normal
e.g. human hemoglobin molecule contains two types of polypeptides, alpha and beta, each produced by different genes
Here are the gene clusters, located on two chromosomes
Alpha locus
Two alpha globin genes, essentially identical
Zeta globin genes are expressed early in development and are part of fetal hemoglobin
Beta locus
Two beta globin genes that are part of adult hemoglobin
Plus other genes expressed earlier in development, as shown in table
|
Embryonic
hemoglobins |
Chain
composition |
|
Embryonic gower 1 |
zeta(2), epsilon(2) |
|
Embryonic gower 2 |
alpha(2), epsilon
(2) |
|
Embryonic |
zeta(2), gamma (2) |
|
Fetal
hemoglobin (HbF) |
alpha(2), gamma(2) |
|
Adult
hemoglobins |
|
|
hemoglobin A
(HbA) |
alpha(2),
beta(2) |
|
Minor
hemoglobin A2 (HbA2) |
alpha(2),
delta(2) |
One allele of the polypeptide HbA produces HbS hemoglobin
Sickling hemoglobin
A person homozygous for HbS has sickle-cell trait
Causes rbcs to collapse and become angular
Sickled rbc phenotype: HbSHbS genotype

Normal rbc phenotype: HbA__ genotype

Sickled cells don’t flow smoothely and create clots, restricting blood flow in organs throughout the body
But, a person heterozygous for HbS is more resistant to malaria
Heterozygote advantage